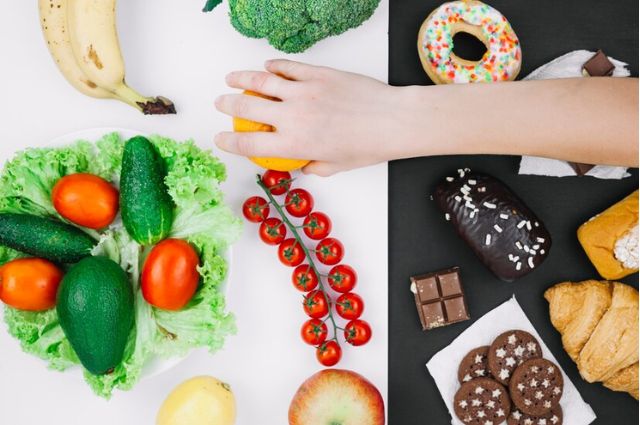
Maintaining a healthy lifestyle is crucial for longevity and overall well-being. Two of the most common health concerns that many individuals face are high cholesterol and high blood pressure. These conditions can lead to serious complications if left unchecked, including heart disease, stroke, and kidney problems. Fortunately, adopting a nutritious diet and making positive lifestyle changes can go a long way in preventing and managing these health issues. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore practical strategies to help you eat smart and live long.
Understanding Cholesterol and Blood Pressure
Cholesterol
Cholesterol is a waxy substance found in your blood and cells. While your body needs some cholesterol for proper function, an excessive amount can lead to the buildup of plaque in your arteries, increasing your risk of heart disease and stroke. There are two main types of cholesterol:
- Low-Density Lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol, known as “bad” cholesterol, can contribute to plaque buildup.
- High-Density Lipoprotein (HDL) cholesterol, or “good” cholesterol, helps remove LDL cholesterol from your arteries.
Blood Pressure
Blood pressure is the force of blood pushing against the walls of your arteries. When this force is consistently high, it can damage your blood vessels and increase the risk of heart disease, stroke, and other health problems. Maintaining a healthy blood pressure level is must for overall well-being.
Dietary Strategies for Prevention
Limit Saturated and Trans Fats
Saturated and trans fats can raise your LDL (bad) cholesterol levels and increase your risk of heart disease. Limit your intake of high cholesterol foods such as fried foods, processed snacks, and baked goods made with partially hydrogenated oils. Instead, shift your emphasis to including nutrient-dense fats like those in avocados, nuts, and olive oil.
Increase Fiber Intake
Fiber is an essential nutrient that can help lower cholesterol levels and improve heart health. Aim to consume a variety of high-fiber foods, such as whole grains, fruits, vegetables, and legumes. Soluble fiber, found in foods like oats, Green apples, and beans, can be particularly effective in lowering LDL cholesterol levels.
Choose Lean Protein Sources
Lean protein sources like fish, poultry, legumes, and low-fat dairy products can help you maintain a healthy weight and promote cardiovascular health. Avoid processed meats high in saturated fat and sodium, and opt for plant-based protein sources like lentils, chickpeas, and tofu.
Reduce Sodium Intake
Excessive sodium consumption can contribute to high blood pressure. Limit your intake of processed foods, salty snacks, and prepared meals, and opt for fresh, whole foods whenever possible. Be mindful of hidden sources of sodium, such as canned soups, condiments, and frozen meals.
Incorporate Potassium-Rich Foods
Potassium is a mineral that can help counterbalance the effects of sodium and lower blood pressure. Include potassium-rich foods like bananas, sweet potatoes, spinach, tomatoes, and low-fat dairy products in your diet. Potassium can also be found in various nuts, seeds, and legumes.
Lifestyle Changes for Better Health
Exercise Regularly
Physical activity can help lower cholesterol levels, reduce blood pressure, and improve cardiovascular health. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity physical activity or 75 minutes of vigorous exercise weekly. Swimming, brisk walking, cycling, or dancing are great options to keep your heart healthy.
Maintain a Healthy Weight
Being overweight or obese can increase your risk of high cholesterol, high blood pressure, and other health problems. Adopt a balanced diet and regular exercise routine to achieve and maintain a healthy weight. Losing even a small amount of weight can significantly improve your cholesterol and blood pressure levels.
Quit Smoking
Smoking is a significant risk factor for heart disease and can contribute to high blood pressure. If you smoke, consider seeking professional help to quit and improve your overall health. Quitting smoking can have immediate and long-term benefits for your cardiovascular system.
Manage Stress
Chronic stress can negatively affect your cardiovascular system, including increased blood pressure and cholesterol levels. Practice stress-management techniques like meditation, yoga, deep breathing exercises, or engaging in relaxing and enjoyable activities. Prioritizing self-care and finding healthy ways to cope with stress can positively impact your overall well-being.
Limit Alcohol Consumption
While moderate alcohol consumption may have some potential health benefits, excessive drinking can raise your blood pressure and contribute to weight gain, increasing your risk of heart disease. If you do consume alcohol, do so in moderation and always consult with your healthcare provider.
Monitoring and Treatment
In addition to lifestyle modifications, it’s essential to monitor your cholesterol and blood pressure levels regularly. Your healthcare provider may recommend screenings and tests to assess your risk and determine if medical intervention is necessary. In some cases, medications may be prescribed to help manage high cholesterol or high blood pressure in conjunction with dietary and lifestyle changes.
Conclusion
Preventing high cholesterol and high blood pressure is essential for maintaining good health and reducing your risk of serious conditions like heart disease and stroke. By adopting a nutritious diet rich in whole, unprocessed foods, engaging in regular physical activity, and making positive lifestyle changes, you can take control of your well-being and pave the way for a longer, healthier life. Remember, small steps can lead to significant improvements, so start implementing these strategies today and enjoy the benefits of a heart-healthy lifestyle.