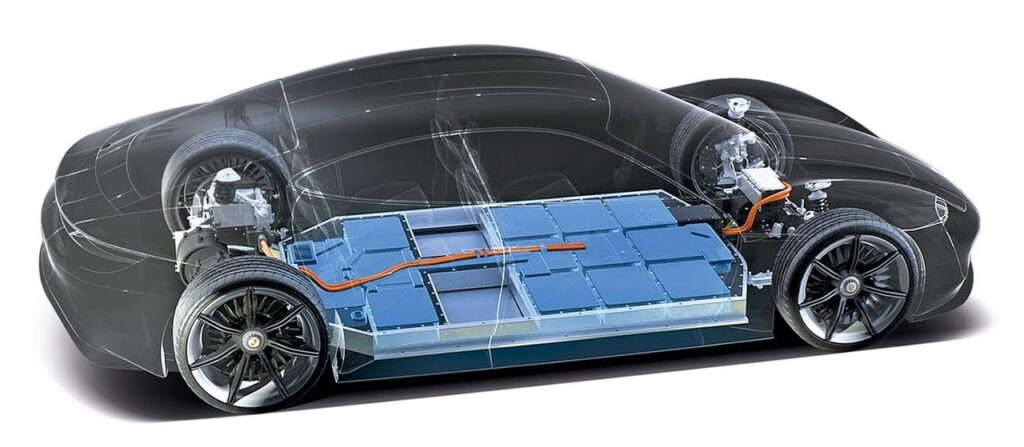
Electric vehicles (EVs) have grown in popularity in recent years, and with this, there has been an increase in interest in the technology that powers these vehicles. One of the key components of an electric vehicle is the battery. In this blog, we’ll explain what a battery is, how it works in an EV, and why it is important.
What is a Battery?
A battery is a device that stores electrical energy in a chemical form and converts it to electrical energy when needed. Batteries are used in a wide range of applications, including powering portable electronics and providing backup power in case of a power outage. In an electric vehicle, the battery is the primary source of power for the vehicle’s electric motor.
How Do Electric Vehicle Batteries Work?
Electric vehicle batteries are typically made up of many smaller cells, which are connected in series or parallel to create a larger battery pack. Each cell contains an anode, a cathode, and an electrolyte. When the battery is charged, ions move from the cathode to the anode, creating a flow of electrons that can be used to power the vehicle’s electric motor. When the battery is discharged, the process is reversed, and the ions move from the anode to the cathode.
The battery management system (BMS) is an important component of an electric vehicle battery. The BMS is responsible for monitoring the battery’s state of charge, state of health, and temperature, as well as controlling the flow of energy to and from the battery. This helps to ensure the battery operates safely and efficiently.
Why is the Battery Important in an Electric Vehicle?
The battery is a critical component of an electric vehicle, as it provides the power needed to drive the electric motor. The range of an electric vehicle is determined by the capacity of the battery, which is measured in kilowatt-hours (kWh). The higher the capacity of the battery, the longer the range of the vehicle. In addition to the range, the performance of an electric vehicle is also impacted by the battery. A high-performance battery can provide the power needed for quick acceleration and high speeds.
Battery technology is also an important factor in the adoption of electric vehicles. Advances in battery technology have resulted in higher energy densities, longer lifetimes, and faster charging times, which have helped to make electric vehicles more practical and affordable.
Types of Batteries Used
1. Lithium-ion Batteries
Lithium-ion batteries are the most common type of battery used in electric vehicles due to their high energy density, long cycle life, and low self-discharge rate. They are made up of several cells that store energy through a chemical reaction. These batteries have a nominal voltage of 3.6V to 3.7V per cell and can be stacked in series to increase voltage or in parallel to increase capacity.
Parameters:
Energy density: 150-250 Wh/kg
Specific energy: 100-200 Wh/L
Cycle life: 500-1000 cycles
Self-discharge rate: 5-10% per month
Cost: Moderate to high
2. Lead-Acid Batteries
Lead-acid batteries are one of the oldest and most widely used types of batteries. They have been used in electric vehicles since the early days of the industry. These batteries are made up of several cells that store energy through a chemical reaction between lead and sulfuric acid. They have a nominal voltage of 2V per cell and can be stacked in series or parallel to increase voltage or capacity.
Parameters:
Energy density: 30-50 Wh/kg
Specific energy: 30-50 Wh/L
Cycle life: 200-300 cycles
Self-discharge rate: 10-20% per month
Cost: Low
3. Nickel-Metal Hydride (NiMH) Batteries
Nickel-metal hydride batteries are another type of battery that is commonly used in electric vehicles. They have a higher energy density than lead-acid batteries but lower than lithium-ion batteries. They are made up of several cells that store energy through a chemical reaction between nickel and a metal hydride. These batteries have a nominal voltage of 1.2V per cell and can be stacked in series or parallel to increase voltage or capacity.
Parameters:
Energy density: 60-120 Wh/kg
Specific energy: 60-120 Wh/L
Cycle life: 500-1000 cycles
Self-discharge rate: 20-30% per month
Cost: Moderate
Rechargeable Batteries
Rechargeable batteries have become a popular choice for electronic devices in recent years due to their environmental benefits and cost-effectiveness. In India, the demand for rechargeable batteries has also increased as people become more conscious of their impact on the environment. If you’re thinking about making the switch to rechargeable batteries in India, this guide is for you.
Benefits of Using Rechargeable Batteries in India
Using rechargeable batteries has several benefits over disposable batteries, including:
Cost Savings: While rechargeable batteries have a higher upfront cost, they can save you money in the long run as you won’t have to keep buying disposable batteries.
Environmental Sustainability: Rechargeable batteries are better for the environment as they reduce the amount of battery waste that ends up in landfills.
Convenience: Rechargeable batteries can be reused multiple times, so you won’t have to keep running to the store to buy new batteries.
Types of Rechargeable Batteries in India
There are several types of rechargeable batteries available in the Indian market, including:
Nickel-Cadmium (NiCd) Batteries: NiCd batteries are a popular choice for power tools and portable electronics due to their high capacity and long life span.
Nickel-Metal Hydride (NiMH) Batteries: NiMH batteries are commonly used in digital cameras, toys, and other portable electronic devices due to their high energy density.
Lithium-Ion (Li-Ion) Batteries: Li-ion batteries are lightweight and have a high energy density, making them ideal for use in smartphones, laptops, and other portable devices.
Tips for Using Rechargeable Batteries in India
Here are some tips to help you get the most out of your rechargeable batteries in India:
- Charge your batteries fully before first use to ensure maximum capacity.
- Store your rechargeable batteries in a cool, dry place to prevent damage and ensure a longer lifespan.
- Use the appropriate charger for your battery type to avoid overcharging or undercharging.
- Replace your rechargeable batteries once they begin to lose their capacity.
Electric car battery lithium-ion
Electric cars are becoming increasingly popular as people look for more environmentally friendly alternatives to gasoline-powered vehicles. One of the key components of an electric car is its battery, and the most common type of battery used in electric cars is the lithium-ion battery.
Lithium-ion batteries have several advantages over other types of batteries, including their high energy density, longer lifespan, and low self-discharge rate. These properties make them ideal for use in electric cars, where long-lasting, reliable energy storage is essential.
In a lithium-ion battery, lithium ions move back and forth between the positive and negative electrodes during charging and discharging. The positive electrode is typically made of lithium metal oxide, while the negative electrode is made of graphite or another carbon-based material. The electrolyte, which allows the lithium ions to move between the electrodes, is usually a liquid or gel-like substance.
One of the key challenges with lithium-ion batteries is ensuring their safety, as they have been known to catch fire or explode under certain conditions. Manufacturers have implemented various safety features, such as thermal management systems, to mitigate these risks.
Another challenge with lithium-ion batteries is their environmental impact. While they are more environmentally friendly than gasoline-powered vehicles, the production and disposal of lithium-ion batteries can have negative environmental consequences if not managed properly. Recycling programs for lithium-ion batteries are becoming more common, which can help reduce their environmental impact.
Are Electric Car Batteries Bad for the Environment?
Electric car batteries are a critical component of electric vehicles (EVs) and have contributed significantly to the growth of the EV market in recent years. However, there is concern about the environmental impact of these batteries.
Firstly, it is important to understand the materials used in electric car batteries. Lithium-ion batteries are the most common type of battery used in EVs, and they typically contain metals such as lithium, cobalt, nickel, and manganese. These metals are mined from the earth and are often found in countries with weak environmental and labour regulations. The extraction and processing of these metals can lead to environmental damage and human rights abuses.
Secondly, electric car batteries have a limited lifespan and need to be replaced after a certain number of charge cycles. When a battery is no longer suitable for use in a vehicle, it can be recycled, but this process is still in its infancy and is not yet widespread. Most batteries are currently disposed of in landfills or incinerated, which can release harmful chemicals and metals into the environment.
However, it is important to note that the environmental impact of electric car batteries must be considered in the context of the entire life cycle of an electric vehicle. Compared to gasoline-powered vehicles, EVs produce fewer emissions during operation, even when the emissions from the production of the battery are taken into account. Additionally, as the electricity grid continues to transition to cleaner sources of energy, such as wind and solar power, the environmental benefits of electric vehicles will only increase.
Electric vehicle Battery Parameters To Consider
When it comes to electric vehicle (EV) batteries, there are several parameters that are important to consider. These parameters can impact the performance, range, and overall functionality of an EV.
1. Capacity
The capacity of an EV battery is a measure of the amount of energy it can store. The higher the capacity, the more energy the battery can store, and the longer the vehicle can travel on a single charge. Battery capacity is typically measured in kilowatt-hours (kWh).
2. Power
Power is a measure of the rate at which the battery can deliver energy. A battery with high power can deliver energy quickly, which is important for acceleration and other high-demand activities. Power is typically measured in kilowatts (kW).
3. Charging Speed
EV batteries can be charged using a variety of methods, including Level 1, Level 2, and DC fast charging. The charging speed of an EV battery is an important consideration, as it can impact the time it takes to charge the battery. DC fast charging is the fastest charging method and can provide a significant amount of charge in a short amount of time.
4. Temperature
The temperature of an EV battery can impact its performance and lifespan. Batteries operate best within a certain temperature range, and extreme temperatures can cause damage to the battery.
5. Cycle Life
The cycle life of an EV battery is a measure of the number of charge and discharge cycles it can go through before its capacity begins to degrade significantly. A battery with a longer cycle life will last longer and require replacement less frequently.
6. Safety
Battery safety is a critical consideration for EVs, as the battery can pose a risk of fire or explosion in certain conditions. Battery management systems and other safety features are important to ensure the safe operation of an EV.
7. Cost
The cost of an EV battery is an important consideration, as it can impact the overall cost of the vehicle. Battery costs are typically decreasing as battery technology improves and economies of scale are achieved.
Conclusion:
The battery is a critical component of an electric vehicle. It stores electrical energy in a chemical form and converts it to electrical energy when needed. The battery pack is made up of many smaller cells, and the battery management system is responsible for monitoring and controlling the flow of energy to and from the battery. The range and performance of an electric vehicle are impacted by the capacity and technology of the battery. As battery technology continues to improve, we can expect to see more widespread adoption of electric vehicles.
FAQs
While rechargeable batteries can be used in most electronic devices, it’s important to check the device’s manual to ensure compatibility.
Rechargeable batteries are generally safe to use, but it’s important to follow the manufacturer’s instructions for proper use and storage.
The lifespan of rechargeable batteries varies depending on the type and usage. Generally, rechargeable batteries can last anywhere from 500 to 1000 cycles.
Image Credit: EV Battery Design courtesy of Tech Space
Read Next Blog:
How to Apply for Electric Vehicle Subsidy